

The OPD Scan and iTrace allow the user to define the pupil size at which aberrations are to be measured. At each pupil diameter, RMS total aberration, RMS high order aberration, spherical aberration (Z4,0), coma aberration (Z3,-1, Z3,1), trefoil aberration (Z3,-3, Z3,3), and the refraction parameters were measured by each aberrometer.īecause the wavefronts are often expressed in terms of Zernike polynomials, a selection of these polynomials can easily be used for comparison purposes.


These pupil sizes were chosen to represent mesopic and scotopic conditions, respectively. Total aberration and internal optic aberration were measured with each instrument at pupil diameters of 4.0 and 6.0 mm. The two aberrometers compared in this study were the iTrace (Tracey Technology) and the OPD Scan (Nidek, Japan). Tropicamide 0.5% was used when appropriate to test response to pupillary dilatation.
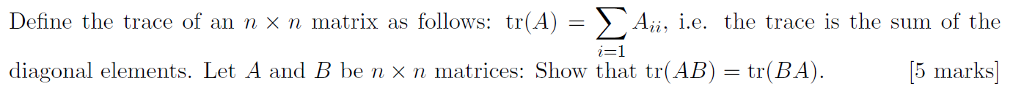
The patient group had an average age of 27☗ years. A history of any kind of contact lens wear in the past month excluded the subject from the study, and eyes with uncorrectable visual acuity below 20/20 were also excluded. Twenty-seven subjects were included in this study, none of whom had any history of ocular abnormalities or prior ocular surgery. Because the devices undergo constant alteration and improvement, we advise potential users to verify all parameters for each model and device. We note that our results only represent the devices as they were made available to us during the study period. We measured ocular total and internal aberration using a Visual Function Analyzer (VFA Tracey Technology) (based on ray tracing can be used with the EyeSys Vista corneal topographer) and an OPD Scan (ARK 10000 Nidek) (based on automatic retinoscopy provides integrated corneal topography and wavefront measurement in one device). Such a comparison is needed to accurately analyze where in the eye light rays are most distorted. Internal aberration refers to light rays that are mainly disturbed in the anterior segment. The total optical aberration of an eye is the sum of all rays entering and exiting the eye. The purpose of this study is to provide a number of technical and practical parameters that may be useful in choosing an aberrometer for daily clinical practice. Making a practical comparison between the available devices is not an easy task because of the variety of principles used, such as ray tracing, Hartmann-Shack, Tscherning, and automatic retinoscopy. 4Īberrometry presents larger applications than just enhancing the quality of the ablation zone in an excimer laser treatment, so the choice of the most appropriate machine depends mainly on the clinical practice. 3Īberrometers are currently the most important tools for estimating optical conditions so that a more complete understanding of optical error can be quantified and corrected. 2 As skills developed for measuring wavefront, it was discovered that HOAs increased following excimer laser ablation of the cornea during refractive surgery. The twentieth century introduced the Zernike polynomials, which could quantitatively analyze optical HOAs in the human eye. 1 These came to be known as high order aberrations (HOAs). In the nineteenth century, Helmholtz found optical errors that could not be corrected using existing optical theory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
